What is 3D printing and how does it work?
Share
3D printing is a technology that has changed the way we create objects, allowing hobbyists and large companies to manufacture everything from small prototypes to fully functional products. But what is 3D printing really and how does it work? In this guide we will explain the basics of this incredible technology, in a simple and clear way.
What is 3D printing or additive manufacturing?
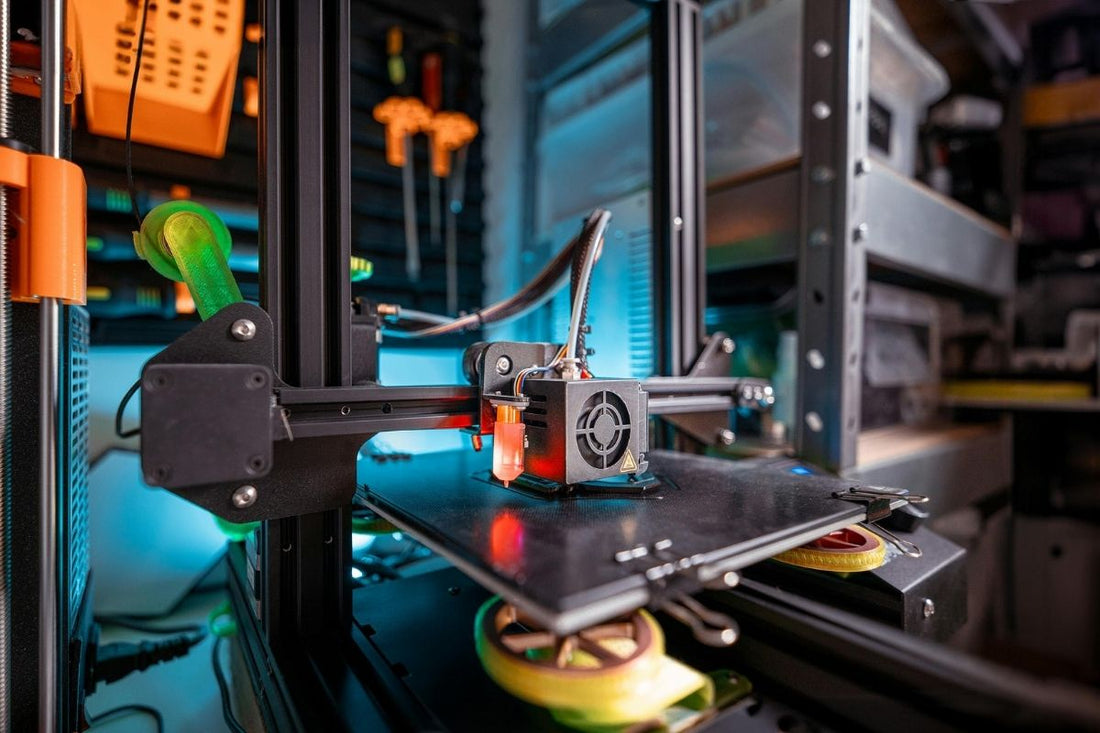
3D printing , also known as additive manufacturing , is a technology that allows three-dimensional objects to be created layer by layer from a digital design. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which typically rely on machining (removing material from an initial piece), 3D printing adds material only where it is needed, allowing for more efficient manufacturing with less waste.
How does 3D printing work?
Creating the 3D Design: The first step in 3D printing is creating a digital model of the object you want to make. This is done using 3D modeling software , such as Tinkercad, Fusion 360, or Blender. If you're new to designing, you can download pre-made models from websites like Thingiverse or MyMiniFactory, where thousands of users share their designs for free.- PLA (Polylactic Acid) – A biodegradable plastic that is easy to use and perfect for beginners.
- ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene): Stronger and suitable for objects that require durability, although it is more difficult to print.
- Liquid resins: Used in resin 3D printers, they offer a smoother, more detailed finish, although they require post-processing.
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers: These use a 3D printer filament that is heated and extruded through a nozzle, creating each layer as the material cools and solidifies.
- SLA (Stereolithography) printers: use liquid resin that is cured layer by layer with ultraviolet light, producing a solid object.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) printers: use 3D printing powder instead of filament, which is melted with a laser to form solid layers.
- Removing Supports: Some prints require temporary supports that are removed once the print is complete.
- Sanding: If the surface is not completely smooth, you can sand it to get a smoother finish.
- UV Curing (on resin printers): Resin prints need to be exposed to ultraviolet light to fully cure and harden.
Advantages of 3D printing
3D printing has several advantages that have made it a key technology:
- Personalization: you can create unique objects tailored to specific needs, from prototypes to final products.
- Reduced waste: Unlike subtractive manufacturing methods (such as carving), 3D printing uses only the material needed, reducing waste.
- Easy access to manufacturing: With a 3D printer, anyone can become a manufacturer from their own home.
Applications of 3D printing or additive manufacturing
The applications of 3D printing are very broad and cover various fields, from industry to the home. Here are some examples:
- Rapid prototyping: Industrial designers can prototype their ideas in a matter of hours, quickly testing different versions before arriving at a final product.
- Personalized Toys: Families can print personalized toys or replacement parts for broken items.
- Medical industry: It is used to create custom prosthetics, dental implants and even organs and tissues in research.
- Fashion and art: Fashion designers and artists have embraced 3D printing to create unique pieces and revolutionize the creative process.
3D printing is a technology that has opened up new possibilities for creating objects, allowing anyone, from beginners to professionals, to make things that were previously only accessible to large factories. Now that you understand how it works, you are one step closer to starting your own 3D printing project. The possibilities are endless!
If you need guidance with a 3D design or model, or are interested in printing a piece, do not hesitate to contact us and we will advise you in a personalized way. Bring your ideas and projects to life at Printatonic .